Gas Development and Commercialization: Driving Energy and Economic Growth
Gas development and commercialization are vital for meeting the world’s growing energy needs. This process involves exploring, extracting, processing, and marketing natural gas. By turning raw gas into a market-ready product, countries can strengthen their energy security and boost their economies. The development process requires careful planning, advanced technology, and strong safety measures.
Natural gas is a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, making it a key player in the global energy transition. However, success in gas development and commercialization depends on balancing profitability, environmental responsibility, and community benefits.
Stages of Gas Development
1. Exploration and Appraisal
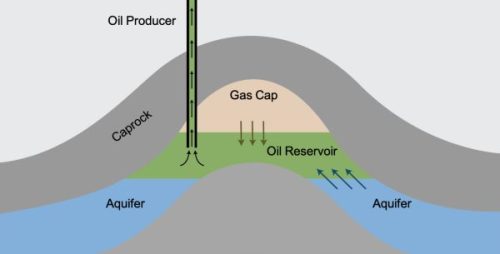
This is the first step in gas development is exploration. Companies use seismic surveys and geological studies to locate potential reserves. Once finding a promising site, proceed with driiling wells to confirm the size and quality of the gas reservoir. This stage helps determine if the project is commercially viable.
2. Field Development
After confirming a viable reserve, field development begins. This involves designing well pads, installing equipment like the Christmas tree wellhead, and building infrastructure for gas collection. Safety measures, such as cellar boxes around the wellhead, are essential to contain spills and protect the environment.
3. Production Operations
Once wells are operational, gas flows to the surface and is processed to remove impurities. The processed gas is then transported via pipelines to markets or liquefaction plants. Continuous monitoring ensures efficiency, safety, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Commercialization Process
Gas Processing and Transportation
Gas commercialization starts with processing, which removes water, carbon dioxide, and other contaminants. High-quality gas is then transported through pipelines or converted into liquefied natural gas (LNG) for overseas shipment. This stage requires coordination between producers, transport operators, and buyers.
Market Development
Producers work to secure long-term contracts with buyers, such as power plants, industrial users, and export markets. Effective market development includes price negotiations, logistics planning, and regulatory compliance. Building trust and reliability with buyers is key to long-term success.
Economic Benefits of Gas Development and Commercialization
Gas projects create jobs, attract foreign investment, and contribute to government revenues through taxes and royalties. Local economies benefit from increased business opportunities and improved infrastructure. Additionally, natural gas can replace more polluting fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving public health.
In developing countries, gas commercialization can help expand electricity access. This supports industries, education, and healthcare, contributing to overall economic growth.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
While natural gas is cleaner than coal or oil, gas development still carries environmental risks. Methane leaks, habitat disruption, and water use are concerns that must be managed. Best practices include regular leak detection, proper waste handling, and minimizing land disturbance.
Safety is a top priority in gas operations. Measures such as emergency shutdown systems, worker training, and protective infrastructure like cellar boxes around wellheads help reduce risks. Compliance with national and international safety standards is essential.
Future Outlook for Gas Development and Commercialization
The demand for natural gas is expected to grow in the coming decades, especially in Asia and Africa. New technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) and digital monitoring systems, will improve efficiency and reduce emissions. However, competition from renewable energy sources will require the gas industry to innovate and maintain cost-effectiveness.
Governments and companies must work together to ensure that gas development benefits society while protecting the environment. This includes transparent regulations, fair revenue sharing, and investment in cleaner technologies.
Gas development and commercialization play a crucial role in global energy supply and economic growth. From exploration to market delivery, each stage demands careful planning, advanced technology, and strong safety measures. When managed responsibly, natural gas offers a cleaner, reliable energy source that can support the transition to a low-carbon future.
By combining economic opportunities with environmental care, gas development and commercialization can continue to power industries, communities, and economies worldwide.